

These findings suggest a need to re-evaluate MoCA cutoff performance in minority populations. found that about 80% of their cohort of community-dwelling African Americans fell below the threshold. found that over 90% of their cohort of African Americans with type 2 diabetes participating in the study of type 2 diabetes and cognitive function screened as “positive” for cognitive impairment. For instance, using the recommended cutoff of 26, Sink et al. Studies that included minority participants found that the originally established cutoff of 26 may result in a high likelihood of classifying normal minority individuals as cognitively impaired. MoCA performance in minority groups has not been widely studied most studies examining the MoCA and its subtests were limited to Caucasian samples.

Although it is widely accepted that the MoCA is better than the MMSE for detection of MCI, ,, some studies suggest that the cutoff of 26 results in a high proportion of normal individuals being classified as cognitively impaired. The MoCA has a high sensitivity for detection of MCI in patients who would score as normal on the Mini-Mental State Examination (MMSE), another widely used tool to assess cognitive impairment using a cutoff of 26 for MCI the MoCA had a sensitivity of 90% whereas the MMSE had a sensitivity of 18%. Scored of 30 points, it has a one-point educational adjustment (addition) for individuals with ≤12 years of education. Administered by a trained health professional, the MoCA takes approximately 10 minutes to complete and has items on orientation, attention, verbal memory, language, visuospatial function, and executive function. The MoCA was developed as a screening tool to distinguish between normal cognition and MCI. Screening is essential for early detection of MCI and AD. Early detection also helps physicians deliver better care and manage comorbid conditions that often occur with greater age. Yet early detection of AD gives individuals time to express their wishes, build a care team, create advance health directives, make legal and financial arrangements, and enroll in clinical trials before their disease progresses to an advanced stage. found that literacy level, rather than years of education, better predicts cognitive decline regardless of race/ethnicity literacy, and years of education are not concordant.Įstimates are that only half of individuals with AD have been diagnosed, and, of those diagnosed, only 33% are aware of their diagnosis. The cognitive reserve theory states that individuals with more educational, occupational, and cognitive engagement are more resilient to damage to their brain, delaying the presentation of symptoms of dementia. Educational attainment is also strongly associated with cognitive reserve. Īmong minority populations, educational attainment is a particularly important risk factor for dementia individuals with fewer years of formal education have a greater risk for developing dementia,. This is a timely topic because the number of racial/ethnic minority group members has increased and will continue to increase in the United States. Measurement bias in the Montreal Cognitive Assessment (MoCA) and other screening tools might inflate rates among minorities. Racial/ethnic minorities are disproportionately at risk for dementia African Americans and Hispanics are more likely to develop AD and other dementias than their non-Hispanic White counterparts, likely because of differences in underlying risk factors,. By diagnosing MCI, health care professionals can act to control cardiovascular risk factors, increase exercise, and initiate cognitive training interventions that may reduce progression from MCI to AD. MCI can be used for early detection and prevention of progression to dementia.
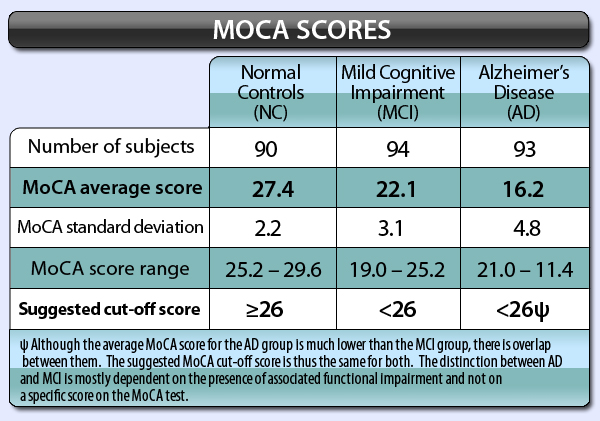
Mild cognitive impairment (MCI), the stage between healthy cognitive aging and dementia, is defined as greater cognitive impairment than is expected for one's age.

Risk factors for AD include nonmodifiable factors, such as older age, family history, and the presence of the apolipoprotein E ( APOE)-ε4 gene, and potentially modifiable risk factors, including low educational attainment, low socioeconomic status, hypertension, smoking, diabetes, depression, and low social and cognitive engagement. Alzheimer's disease (AD), the most common form of dementia, affected approximately 5.5 million Americans in 2017 this number is projected to increase to as high as 16 million by 2050.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
